GCSE Biology - AQA
1.1.7 - Structures of Eukaryotic Cells
Jump to:
Structures of Eukaryotic Cells
There are certain features which all eukaryotic cells share. They are all relatively large cells (compared to prokaryotic cells), and they all have their DNA enclosed in a nucleus.
In terms of sub-cellular structures, all eukaryotic cells have a cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, ribosomes and mitochondria.
Some types of eukaryotic cells also have other sub-cellular structures: plant cells and algal cells have chloroplasts, a vacuole and a cell wall.
The structures of animal, plant and algal cells are shown below. The functions of the various sub-cellular structures will be explained on a later page. For now, we will just focus on which cells have which sub-cellular structures.
Animal cells
Animal cells have the following sub-cellular structures:
- Nucleus - which contains the cell's DNA.
- Cell membrane - the membrane which surrounds the cell.
- Cytoplasm - the fluid which fills the cell.
- Ribosomes - which appear as small dots in the cytoplasm.
- Mitochondria - round, red structures within the cytoplasm.

Diagram of an animal cell, with its sub-cellular structures labelled.
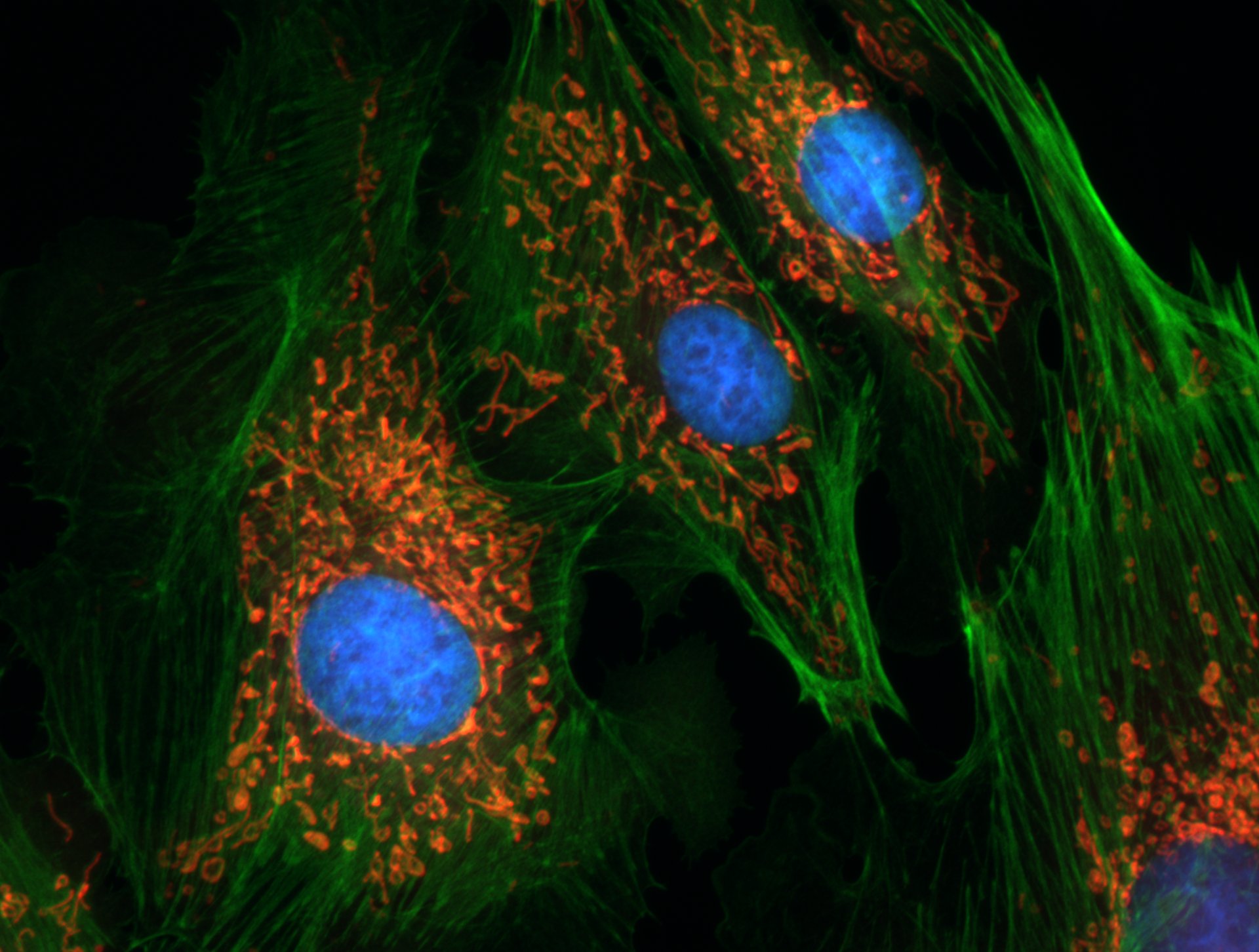
Microscope image of animal cells. These cells are from a cow's pulmonary artery. They have been stained with three fluorescent stains: one that turns the nucleus blue, one that turns the mitochondria red and one that turns a protein called actin green. Image: Erin Rod on Wikimedia Commons (CC BY 4.0)
Plant cells
Plant cells have all of the same sub-cellular structures as animal cells. In addition, they have:
- Chloroplasts - round, green structures within the cytoplasm.
- Vacuole - a large sac containing a fluid called cell sap.
- Cell wall - A rigid wall around the outside of the cell membrane. It is made of a substance called cellulose.

A plant cell, with its sub-cellular structures labelled.
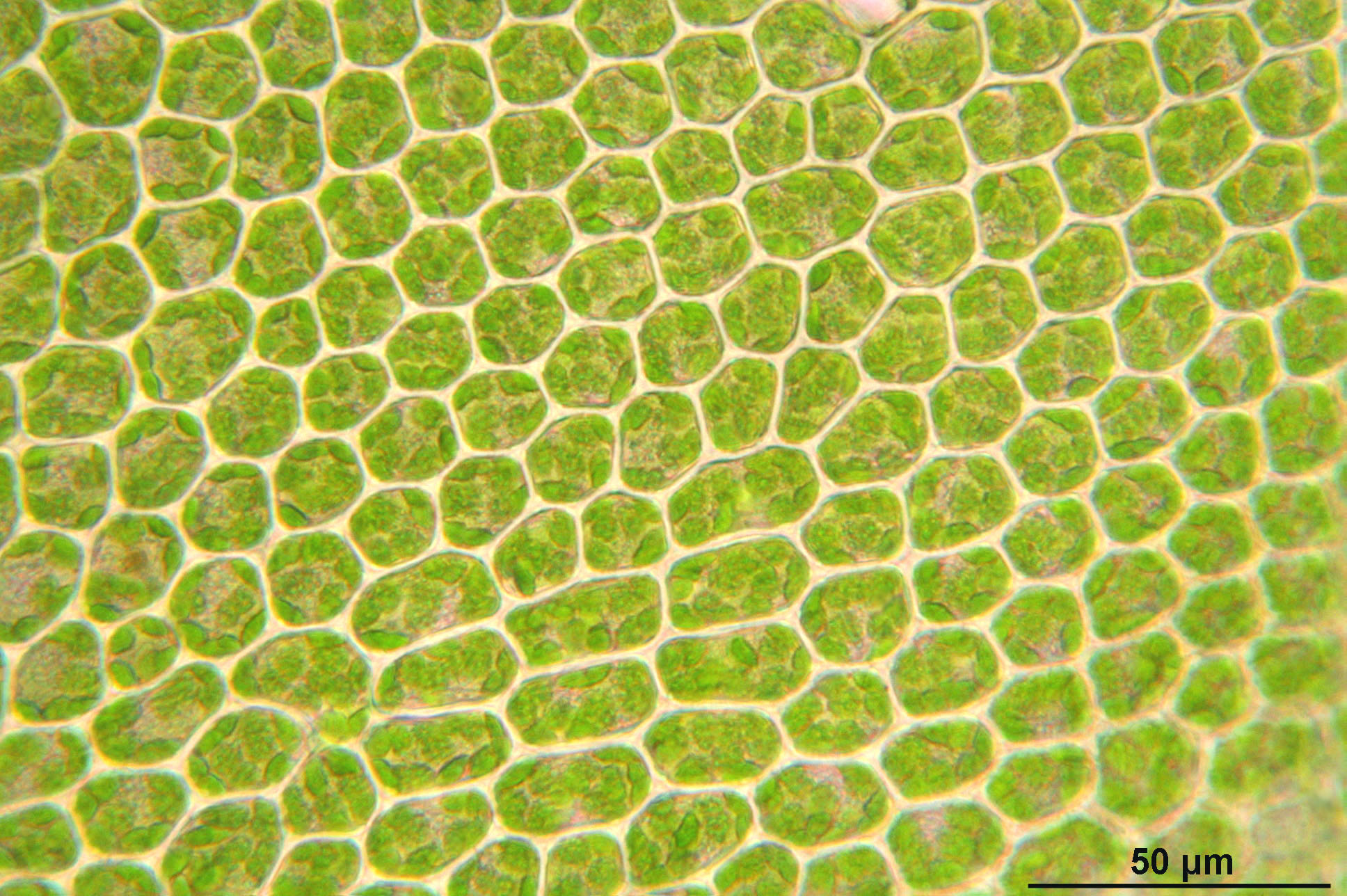

Light microscope image of cells from a plant called Hart's-tongue Thyme-moss. Cell walls and chloroplasts are visible.
Algal cells
Algal cells (the cells of algae) have all of the same sub-cellular structures as plant cells, including a cell wall made out of cellulose. This is because plants and algae are closely related.

An algal cell, with its sub-cellular structures labelled.
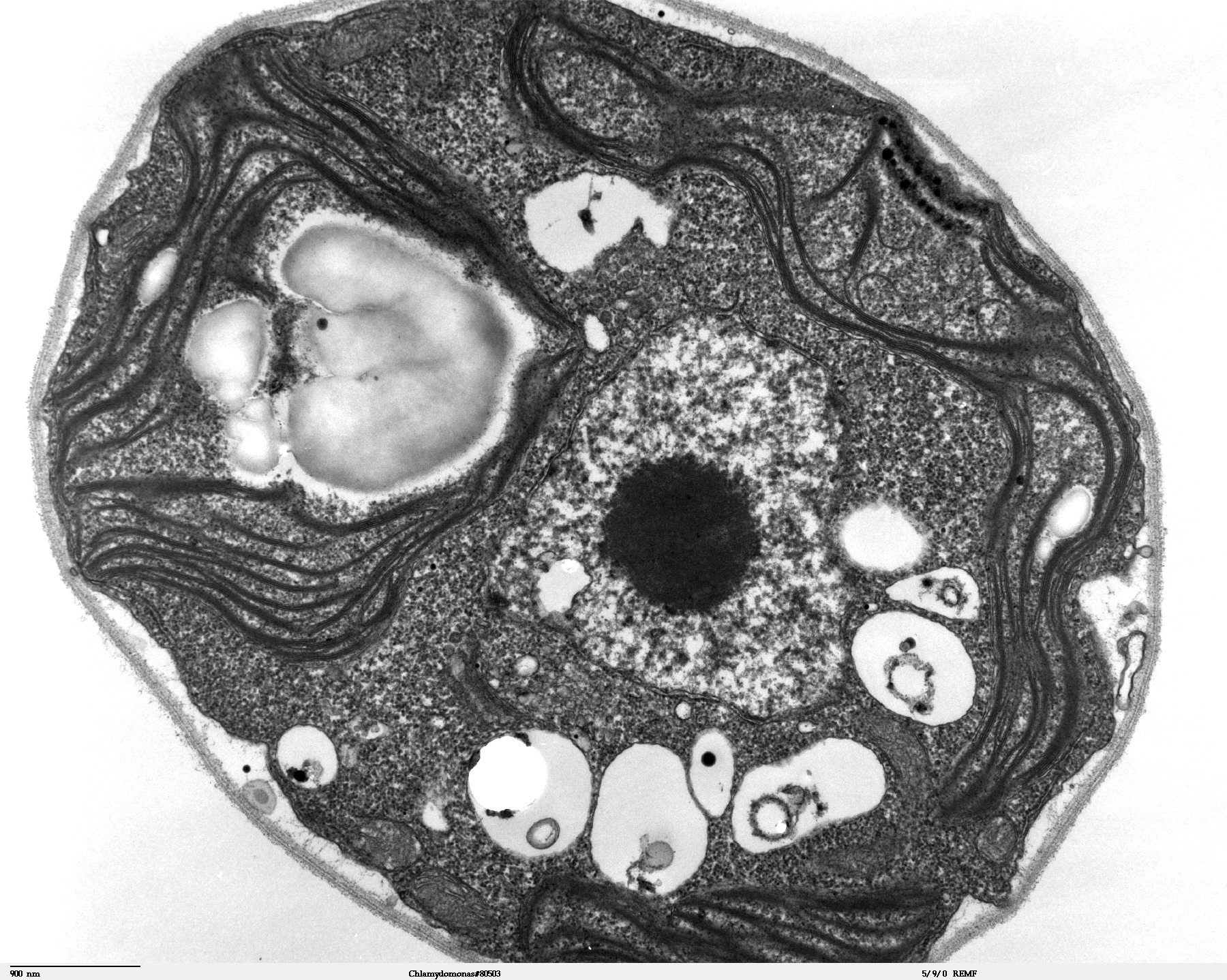
An algal cell viewed through an electron microscope
Flashcards
Flashcards help you memorise information quickly. Copy each question onto its own flashcard and then write the answer on the other side. Testing yourself on these regularly will enable you to learn much more quickly than just reading and making notes.
1/3
What features do all eukaryotic cells share?
2/3
Which sub-cellular structures are found in animal cells?
3/3
Which sub-cellular structures are found in plant and algal cells?
Next Page
1.1.8 - Structures of Prokaryotic Cells
Previous Page
1.1.6 - Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells
Return to course page
Donate
Please consider donating to support Mooramo. I am one person doing this whole project on my own - including building the site, writing the content, creating illustrations and making revision resources. By making a one-time or repeating donation you will buy me time to work on Mooramo, meaning that I can get new content on here more quickly.
Donate