GCSE Biology - AQA
1.2.6 - Xylem Cells
Jump to:
Xylem Cells
In a plant, the water and mineral ions which are absorbed by the roots need to be transported up to the rest of the plant. They do this by travelling through a series of tubes called the xylem.
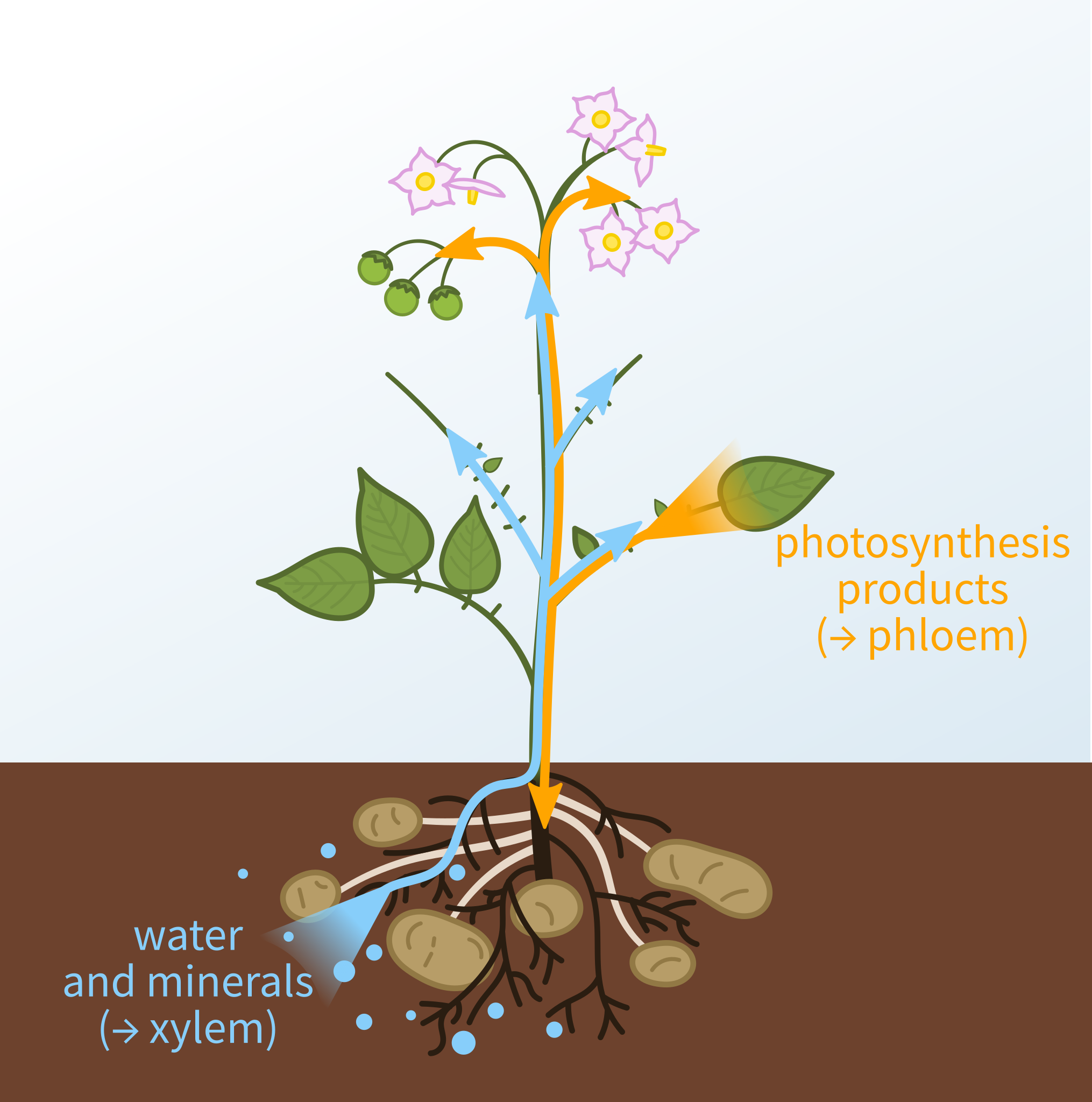
The xylem, shown in blue in this diagram, carries water and mineral ions from the roots up to the rest of the plant. Image: Xylem and phloem diagram.svg by Nefronus on Wikimedia Commons (CC BY-SA 4.0 - creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/deed.en).
The xylem will be covered in more detail later in the course when we look at transport in plants. For now, we will just focus on the cells that make up the xylem and their adaptations.
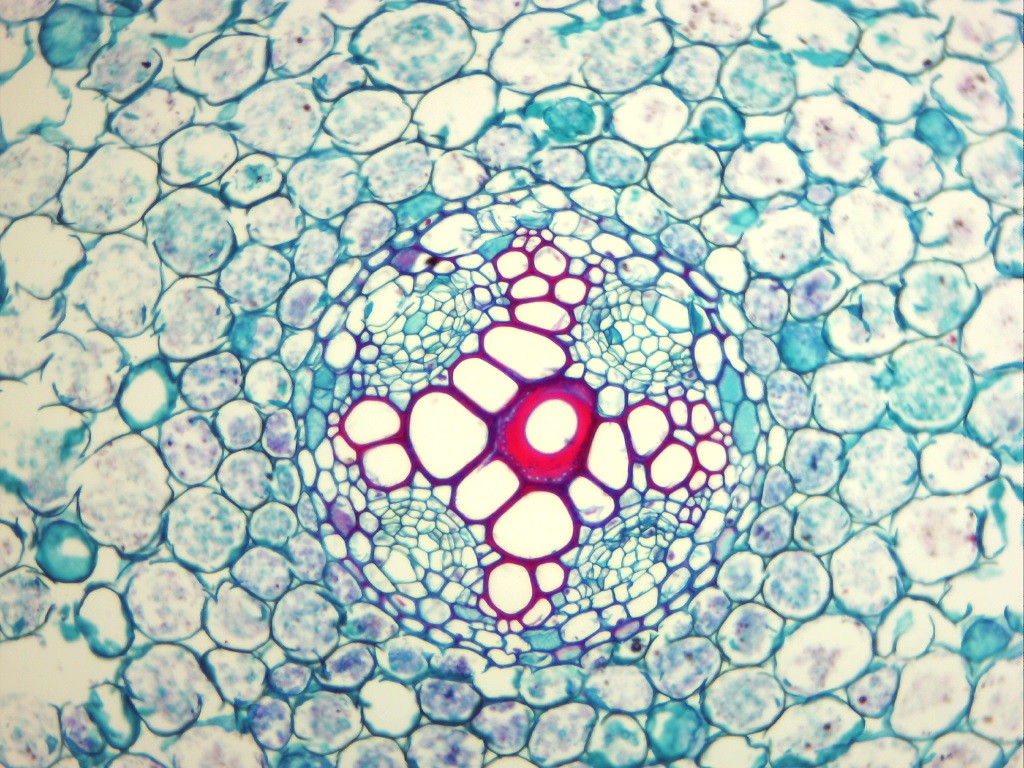
Microscope image of a cross section of a plant root. The cells have been treated with a stain that colours the cell walls. The xylem cells are the ones in the centre that form a cross shape. Their cell walls have been turned red by the stain. Image: Xylem Stained.jpg by Nicholas.H.Hale on Wikimedia Commons (CC BY-SA 4.0 - creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/deed.en).
The function of a xylem cell is to transport water and mineral ions.
Adaptations of xylem cells
A diagram of a xylem cell is shown below:

A xylem cell
The adaptations of xylem cells include the following:
| Adaptation | How it enables a xylem cell to carry out its function of transporting water and mineral ions. |
|---|---|
| It is a hollow, dead cell with no cytoplasm or other contents. | This allows water and mineral ions to flow through it easily. |
| It has no end walls. | This enables it to join together with other xylem cells to form a continuous tube for water and mineral ions to flow through. |
| It has a substance called lignin in its cell wall. | The lignin in the cell wall strengthens the cell to prevent it from collapsing. It also helps to waterproof the cell to prevent water from leaking out. |
Flashcards
Flashcards help you memorise information quickly. Copy each question onto its own flashcard and then write the answer on the other side. Testing yourself on these regularly will enable you to learn much more quickly than just reading and making notes.
1/5
What is the function of a xylem cell?
2/5
What adaptations does a xylem cell have that enable it to carry out its function?
3/5
How does being a dead, hollow cell enable a xylem cell to carry out its function?
4/5
How does having no end walls enable a xylem cell to carry out its function?
5/5
How does having lignin in its cell wall enable a xylem cell to carry out its function?
Donate
Please consider donating to support Mooramo. I am one person doing this whole project on my own - including building the site, writing the content, creating illustrations and making revision resources. By making a one-time or repeating donation you will buy me time to work on Mooramo, meaning that I can get new content on here more quickly.
Donate