GCSE Biology - AQA
1.2.4 - Muscle Cells
Jump to:
Muscle Cells
The function of a muscle cell is to contract in order to generate movement. This could be to move body parts, such as arms and legs, or it could be to bring about movement with the body - such as moving food through the digestive system.
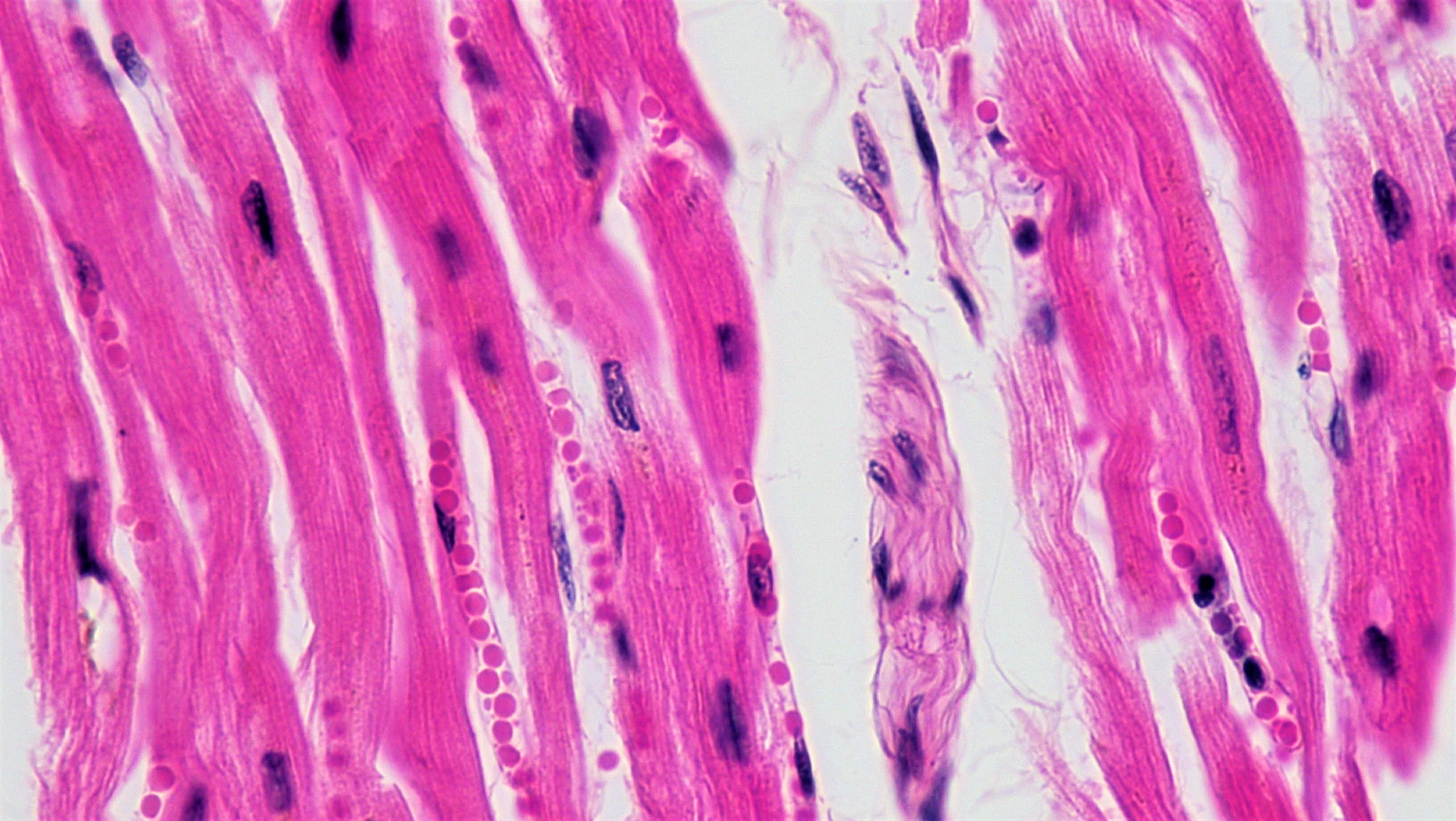
Microscope image of heart muscle cells. The cells have been stained to show the cytoplasm (pink) and the nuclei (blue).
Adaptations of muscle cells
A diagram of a muscle cell is shown below:

A muscle cell's adaptations include its protein filaments, its many mitochondria and its store of glycogen.
The adaptations of muscle cells include the following:
| Adaptation | How it enables a muscle cell to carry out its function of contracting to generate movement |
|---|---|
| It contains protein filaments, made out of proteins called actin and myosin. | These protein filaments can slide over each other in order to bring about contraction. |
| It has many mitochondria. | The many mitochondria provide energy through aerobic respiration. This energy is used in contraction. |
| It has a store of glycogen. | This glycogen can be broken down into glucose, which can then be broken down through respiration to release energy for contraction. |
Flashcards
Flashcards help you memorise information quickly. Copy each question onto its own flashcard and then write the answer on the other side. Testing yourself on these regularly will enable you to learn much more quickly than just reading and making notes.
1/5
What is the function of a muscle cell?
2/5
What adaptations does a muscle cell have that enable it to carry out its function?
3/5
How do a muscle cell's protein filaments enable it to carry out its function?
4/5
How does having a large number of mitochondria enable a muscle cell to carry out its function?
5/5
How does a muscle cell's glycogen store enable it to carry out its function?
Donate
Please consider donating to support Mooramo. I am one person doing this whole project on my own - including building the site, writing the content, creating illustrations and making revision resources. By making a one-time or repeating donation you will buy me time to work on Mooramo, meaning that I can get new content on here more quickly.
Donate